Pumps
There are several types of pumps used in oil and gas operations, including:
These pumps are commonly used for low-viscosity fluids with moderate flow rates, such as crude oil, refined products, and water. Centrifugal pumps generate high flow rates by converting rotational energy from an electric motor or engine into kinetic energy.

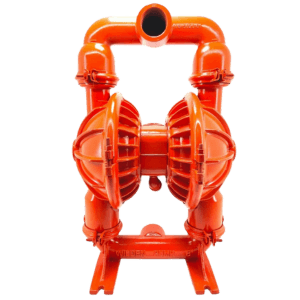
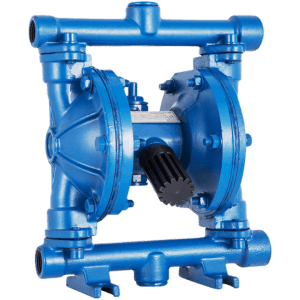
Diaphragm pumps handle oils, chemicals, and corrosive fluids. These pumps have a flexible, reciprocating diaphragm that pushes the fluid through the pump.
Positive displacement pumps handle viscous fluids such as bitumen, heavy crude, and molasses. These pumps operate by trapping a fixed fluid volume between the pump’s cavities and moving it through the pipeline.

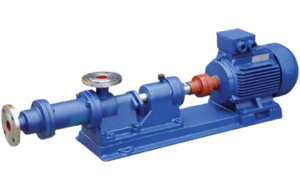
Screw pumps are used for pumping oil or high-viscosity fluids. These pumps move fluids through rotating screws or spirals placed inside the pump’s casing or tube.
Submersible pumps are used for wells and reservoirs. These pumps are placed at the bottom of the reservoir and are designed to withstand high pressures and corrosive fluids.

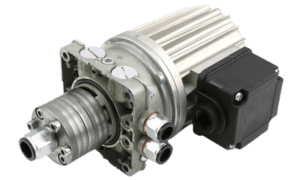
Gear pumps are used for handling low-viscosity fluids such as refined products and light crude oil.
Air-operated pumps use compressed air to move and transfer oil and other viscous fluids. These pumps are popular for their low maintenance requirements and rugged design.